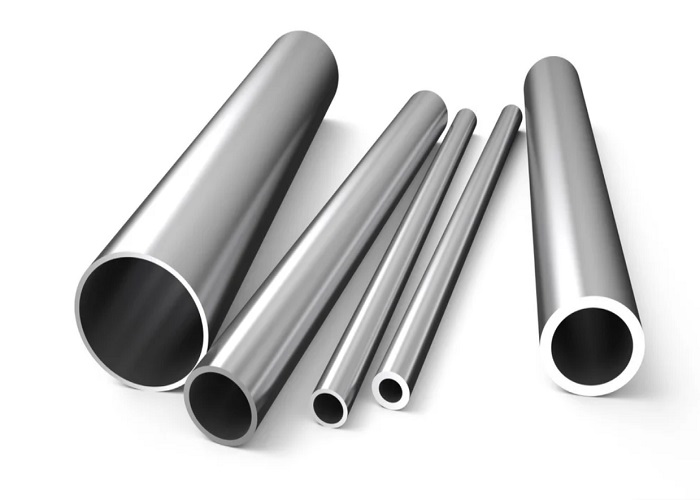
Titanium tubes come in various forms, including seamless, welded, and extruded. They are further classified based on their shape, such as round, square, and rectangular, offering versatility for diverse applications.
Seamless Titanium Pipes
Seamless titanium pipes are manufactured without any welding seams, resulting in a uniform structure that enhances strength and corrosion resistance. These pipes are renowned for their high precision, making them ideal for critical applications such as aerospace components, chemical processing, and medical implants.
Welded Titanium Pipes
Welded titanium pipes are fabricated by welding together titanium sheets or strips, offering a cost-effective alternative without compromising quality.
Both seamless and welded titanium pipes adhere to rigorous specifications, including ASTM standards, ensuring consistent quality and performance. With their impressive strength-to-weight ratios, excellent corrosion resistance, and versatility in size and configuration, seamless and welded titanium pipes are indispensable components in numerous industries, driving innovation and progress worldwide.
We pride ourselves on offering top-quality titanium tubes and pipes, meeting stringent industry standards. With our diverse range of forms and specifications, we provide tailor-made solutions to suit your specific needs, ensuring success in every project.
Pipe Type: Customized seamless tubes and welded tubes
Material: Gr1, Gr2, Gr5, Gr7, Gr9, Gr11, Gr12, Gr18, Gr23, etc.
Standards: GB, ASTM, ASME, AMS, MIL, JIS, DIN.
Applications: Tailored for diverse industries including aerospace, medical implants, chemical processing, and marine structures.
Customization Options: Available in various diameters (6mm to 150mm) and wall thicknesses (1mm to 4.5mm) to meet unique project requirements.
Welcome to contact us for more customized solutions.
Aerospace and Aviation
Aircraft Airframes
Engine Components
Hydraulic Systems
Medical
Orthopedic Implants
Surgical Instruments
Dental Implants
Kemična predelava
Titanium Heat Exchangers
Reactor Vessels
Pipelines
Marine
Ship Hulls
Submarine Structures
Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms
Automotive
Exhaust Systems
Racing Car Frames
Turbocharger Components
Power Generation
Gas Turbine Components
Heat Transfer Tubing
Nuclear Reactor Systems

Titanium Tubes Grade for your choice!
1. stopnja
is the most ductile and softest titanium alloy. It is a good solution for cold forming and corrosive environments. ASTM/ASME SB-265 provides the standards for commercially pure titanium sheet and plate.
Grade 2
Unalloyed titanium, standard oxygen.
Grade 2H
Unalloyed titanium (Grade 2 with 58ksi minimum UTS).
3. stopnja
Unalloyed titanium, medium oxygen.
Grades 1-4 are unalloyed and considered commercially pure or "CP". Generally the tensile and yield strength goes up with grade number for these "pure" grades. The difference in their physical properties is primarily due to the quantity of interstitial elements. They are used for corrosion resistance applications where cost, ease of fabrication, and welding are important.
Grade 5 also known as Ti6Al4V, Ti-6Al-4V or Ti 6-4
6. razred
contains 5% aluminium and 2.5% tin. It is also known as Ti-5Al-2.5Sn. This alloy is used in airframes and jet engines due to its good weldability, stability and strength at elevated temperatures.
7. razred
contains 0.12 to 0.25% palladium. This grade is similar to Grade 2. The small quantity of palladium added gives it enhanced crevice corrosion resistance at low temperatures and high pH.
Grade 7H
is identical to Grade 7 (Grade 7 with 58ksi minimum UTS).
9. razred
contains 3.0% aluminium and 2.5% vanadium. This grade is a compromise between the ease of welding and manufacturing of the "pure" grades and the high strength of Grade 5. It is commonly used in aircraft tubing for hydraulics and in athletic equipment.
11. razred
contains 0.12 to 0.25% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 12
contains 0.3% molybdenum and 0.8% nickel. This alloy has excellent weldability.
Grades 13, 14, and 15
all contain 0.5% nickel and 0.05% ruthenium.
Grade 16
contains 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 16H
is identical to Grade 16 (Grade 16 with 58 ksi minimum UTS).
Grade 17
contains 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 18
contains 3% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium and 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade is identical to Grade 9 in terms of mechanical characteristics. The added palladium gives it increased corrosion resistance.
Grade 19
contains 3% aluminium, 8% vanadium, 6% chromium, 4% zirconium, and 4% molybdenum.
Grade 20
contains 3% aluminium, 8% vanadium, 6% chromium, 4% zirconium, 4% molybdenum and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grade 21
contains 15% molybdenum, 3% aluminium, 2.7% niobium, and 0.25% silicon.
Grade 23 also known as Ti-6Al-4V-ELI or TAV-ELI
Grade 24
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grade 25
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.3% to 0.8% nickel and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grades 26, 26H, and 27
A hexagon formed from thermal stir welding of a Titanium alloy
all contain 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grade 28
contains 3% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium and 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grade 29
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grades 30 and 31
contain 0.3% cobalt and 0.05% palladium.
Grade 32
contains 5% aluminium, 1% tin, 1% zirconium, 1% vanadium, and 0.8% molybdenum.
Grades 33 and 34
contain 0.4% nickel, 0.015% palladium, 0.025% ruthenium, and 0.15% chromium. Both grades are identical but for minor difference in oxygen and nitrogen content.[30] These grades contain 6 to 25 times less palladium than Grade 7 and are thus less costly, but offer similar corrosion performance thanks to the added ruthenium.
Grade 35
contains 4.5% aluminium, 2% molybdenum, 1.6% vanadium, 0.5% iron, and 0.3% silicon.
Grade 36
contains 45% niobium.
Grade 37
contains 1.5% aluminium.
Grade 38
contains 4% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium, and 1.5% iron. This grade was developed in the 1990s for use as an armor plating. The iron reduces the amount of Vanadium needed as a beta stabilizer. Its mechanical properties are very similar to Grade 5, but has good cold workability similar to grade 9.